16 cores and 30 GB under the hood of Your Jupyter for $0.25 per hour
If You are not very lucky, and at work no n-nuclear monster, which to load your scripts, then this article is for You. Also if You used to run scripts all night (and this morning read that somewhere, forgot the brackets, and 6 hours of computation was gone) — You have the chance to finally meet Amazon Web Services.

In this article I will tell how to start working with EC2. In fact, this step-by-step instruction manual semi-automatic rental spot instance AWS to work with Jupyter notebooks and assembling libraries Anaconda. It will be useful, for example, those in Kaggle competitions still enjoys his toy Mac.
Probably the reaction of everyone who first came to Amazon Web Services — is confused by the abundance of services and virtual machines (which are called instances).
In this tutorial I will show you how to cheaply rent computing AWS instance and quickly set it on the Jupyter server to use as a favorite notebooks. The emphasis will do on the build of Anaconda and machine learning problems, but it is clear that the server can be in different order to use, at least mine bitcoins :)
Motivation: want to quickly (within 5-7 minutes) to access from Jupyter notebooks to compute more serious than the home PC.
Generally there are is a good thing tutorial. The article that You're reading a free translation, with additions. We will write a script that will run each time when you rent a car. And here result for those who are in a hurry.
We are going to rent a spot instance C3.4xlarge, 16 cores and 30 GB RAM.
"Spot" means that in fact we will participate in the auction and set a price per hour of use of the machine, to have access to it for as long as demand does not increase. If the demand will increase and market price will exceed the one we made, the car from us "run away", and suddenly. It is for this reason (instability), many people are afraid to use spot instances, though they can greatly save compared instances "on demand". Same car, but in a more "stable" mode, cost about $0.85/hour, we spend four times less.
Now, about the types of machines. They are well described the AWS documentation, so choose the type With a machine that is optimized for calculations.
the
For a start, register on the website Amazon Web Services. Here instruction will not write — as usual, it will be necessary only to confirm by telephone, and via e-mail. The account will have a credit card bind, but if you are afraid of the expenses, you can instance m4large (2 CPU, 8 Gb RAM) to take over the $0.05/hour.
Go to your AWS console and find the service in Services EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)

The Spot Requests tab click on "Request Spot Instance".
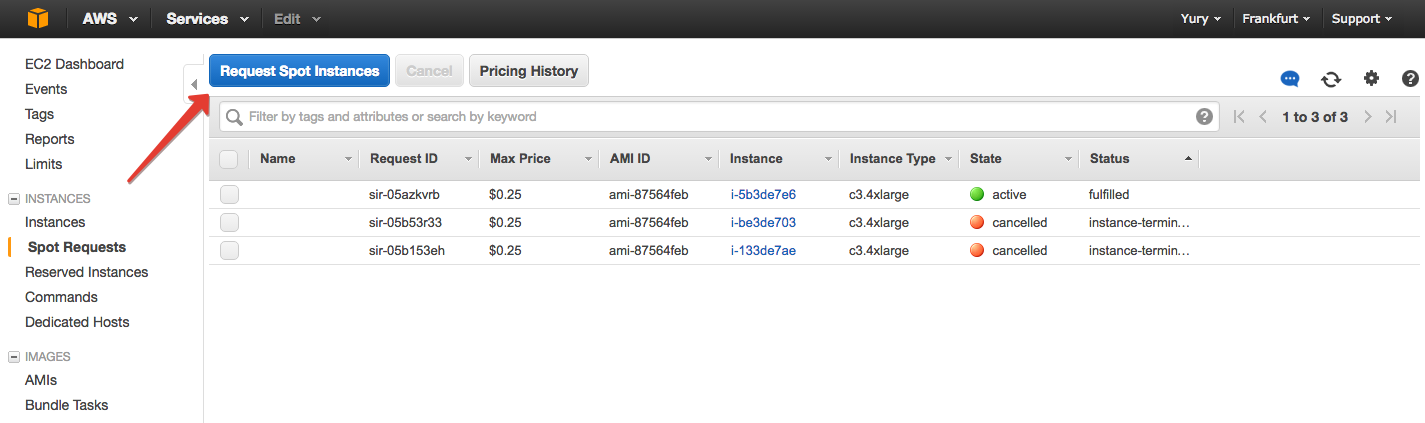
Select the OS type, which will stand on a virtual machine. In General terms: Windows more among *Nix is not so important what to choose, let it be Ubuntu.
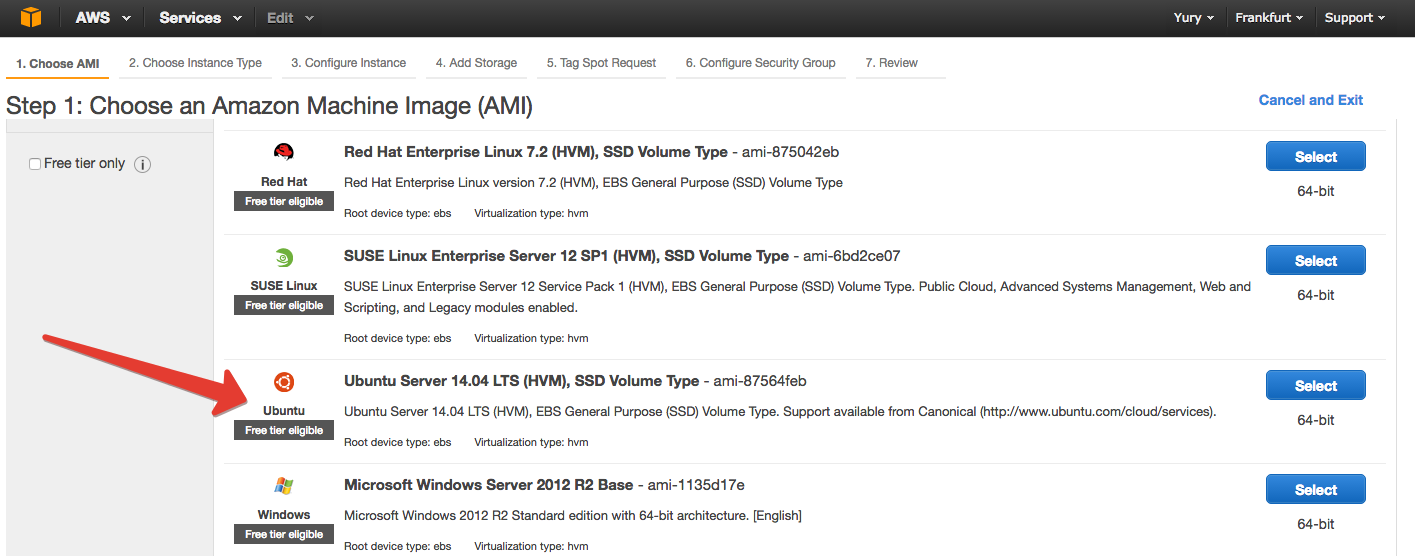
On the next tab, we are asked to choose the actual instance. Here pozalipaesh, posravnivaem (here all explained in detail) and scroll down to C3.4xlarge.

Then the most important thing is to set a price per hour of use dev. We see the current price in the selected regions.

If you see that You have prices much higher than in the screenshot, so now in the current surge region — change the region (in the upper right corner next to Your name). I have yet to successfully use the Frankfurt region, but it is possible to study the statistics to see which regions cheaper and stable prices.
The price is better to assign 1.5 times higher than the current market value of the instance in the region. In this scenario, the price will vary, but rarely exceed stated by You. Accordingly, so the machine is not often will "fall off."
Now connect the storage. Amazon treats thirty GB, so why not take all 30...

Tagging instance can be skipped. And then configure the ports. The main thing — to open the port that we will use under Jupyter server. Let traditionally, it will be 8888. Click "Add rule", leave the option "Custom TCP rule" and specify port 8888. Also added the HTTP and HTTPS protocols and speak, who can listen to ports. It is enough to choose the right Daw My IP.

In the next step generate the key (. pem file) that will us to identify when connecting remotely to the machine through SSH Protocol. It can be called whatever you like — the main thing after downloading to know where he lies in no case (!!!) don't put on GitHub or somewhere else online. Treat it almost like a file to the password of the credit card. Amazon recommends that you periodically update the. pem file (they can have 2 in each region, the second time you download the same key).

Finally, all confirm, wait a few minutes until the instance starts, and the EC2 on the tab "Instances" notice that something has appeared.
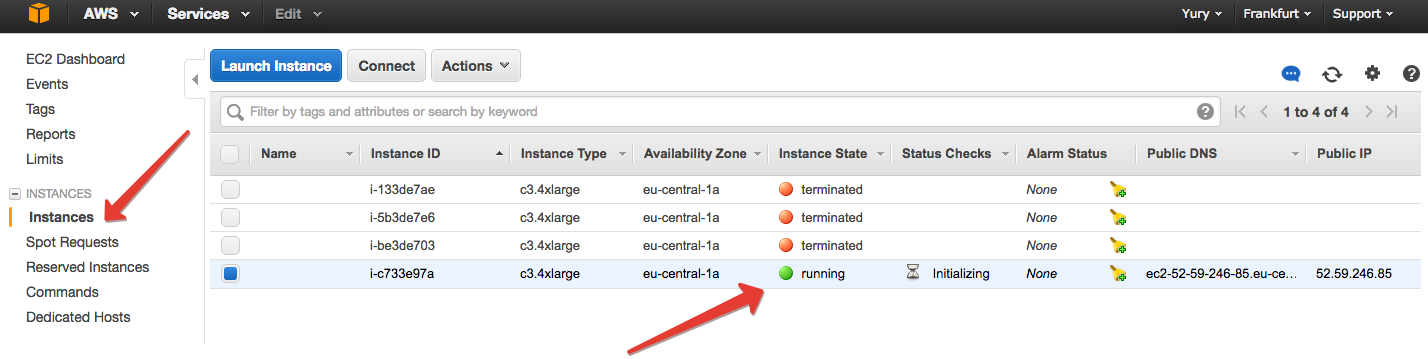
Select the displayed instance and click Connect. Amazon gives instructions on what to do next.
If You're under Windows, then You are reading the article does not end (usually, this is where the tutorials can be read "on Windows? Good luck!"). It is only necessary to read the instructions Amazon how to connect using Putty.
If You are under *NIX, then execute these 2 commands:
the
First taking care that not every one who can access Your. pem file. The second is the actual connection to the virtual reality with its own unique host .
the
If everything went smoothly, you as the user ubuntu will get to the terminal on the remote machine.
You can do anything, run any scripts, but we will focus on the instance setup for machine learning tasks with Jupyter. All commands described below, so that they were easier to understand (and to make sure there were no jokes in the style of rm-rf /) but the second time, and then we will start the bash script.
Download and install Miniconda. It is still much easier to Anaconda, and the necessary libraries we doustanovit (however, seaborn I have not flooded with Anaconda and everything is fine). We machine for a while, hardly more than a few hours, so no perfectionism — install everything into your home directory.
the
Now install all the libraries we want.
the
You can, for example, and Vowpal Wabbit supply (smart linear model, which for large samples is sometimes considered a fast MapReduce implementations).
the
It will not hurt and Git — the repository to download (I use Amazon S3 in this tutorial not considered).
the
Create a certificate to log on Jupyter password — so much safer. Now do it with your hands, the second time this generated certificate will be used by the script.
the
You will be prompted about the user information. In principle it is not necessary to fill in.
Now create the password for Jupyter server.
the
Appears the hash of Your password. Copy it.
the
Finally, create a profile and start the IPython server, pre-specifying in the configuration file, what port we want to use and what addresses are allowed access. Specify the hashed password. You password will be different — need to insert your.
the
The last thing we do only on the remote machine — run IPython server.
(Why IPython and Jupyter not?.. Why certfile explicitly specified? The answer is simple: the crutches. Jupyter didn't want to see the. config file, and then not wanted him to see the settings of the certificate file. See if You and jupyter team starts and without an explicit configuration file and certificate).
the
If all goes well, You'll see at the end read something like this.
the
the
Now go to browser on HOST:8888, where HOST is still the address of your instance. Attention! Protocol needs to be HTTPS, you may also need a confirmation certificate. (For example, in Chrome it is necessary to poke the "more" and confirm on the website).
Enter your password (there is, of course, not hashed, and "normal") and we see a pleasant picture — the file system of Jupyter.

Create a new Notepad and rejoice in the abundance of cores under the hood.

Now back to the terminal (our computer and not the remote machine) and let down on our instance of some dataset. For example, from the Kaggle competition "Forest Cover Type Prediction".
the
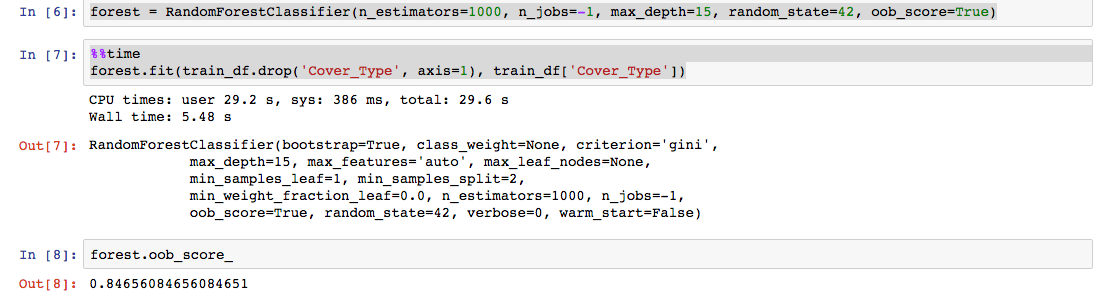
About machine learning, of course, interesting to talk to, but then we just run the Sklearn random forest on the raw data.

Note the parameter n_jobs — here we will use all 16 cores.
1,000 trees of maximum depth 15 learned ~ 5 seconds — 3 times faster than on my MacBook Air with 4 cores and 4 GB of memory. In large samples the difference, of course, will be significant.
the
The process can be automated. Using the Amazon SDK for Python name boto can the backup spot instance runs a script to do that. But until we look at the scripts, which prepare the machine to work with Jupyter after it started.
All this in repository Github.
Just need 3 files:
the
In the correct directory, run:
the
5-7 minutes, that's all! You can work with Jupyter server.
Was about to pour some tea. But! A very important moment!
At the end of work stop your instance.
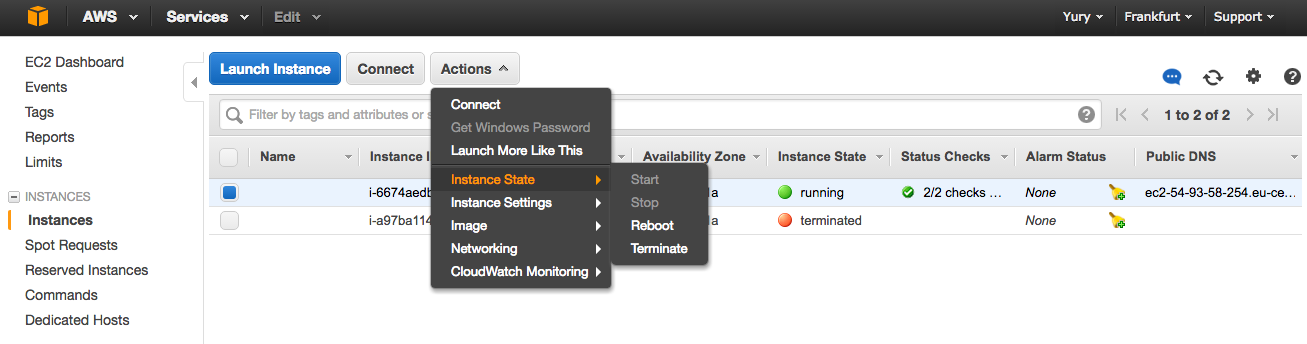
EC2 - > Instances - > Actions -> Instance State -> Terminate.
Terminate it and not stop (although the spot is only available). But if you run instances on demand stop is not completely off the car, can charge money for the data exchange.
Finally it is possible a little to discuss finances. A current account is checked at Amazon by clicking on their name and then on "Billing &Cost Management".
$0.25 / hour is about $25 per month if used 4 hours each weekday. Then everyone decides whether such spending.
Here to advertise and GitHub Student Developer's Pack — I personally, with their help received a certificate to Amazon for $110, still use it. In addition, for serious scientific projects is possible to obtain a grant from Amazon.
the
That's all for now. I think for some it was a jump-start to Amazon Web Services EC2. Let his servos to rest at night!
PS. Comments / advice / sharing of experience / s pull request are welcome.
Article based on information from habrahabr.ru

In this article I will tell how to start working with EC2. In fact, this step-by-step instruction manual semi-automatic rental spot instance AWS to work with Jupyter notebooks and assembling libraries Anaconda. It will be useful, for example, those in Kaggle competitions still enjoys his toy Mac.
Probably the reaction of everyone who first came to Amazon Web Services — is confused by the abundance of services and virtual machines (which are called instances).
In this tutorial I will show you how to cheaply rent computing AWS instance and quickly set it on the Jupyter server to use as a favorite notebooks. The emphasis will do on the build of Anaconda and machine learning problems, but it is clear that the server can be in different order to use, at least mine bitcoins :)
Motivation: want to quickly (within 5-7 minutes) to access from Jupyter notebooks to compute more serious than the home PC.
Generally there are is a good thing tutorial. The article that You're reading a free translation, with additions. We will write a script that will run each time when you rent a car. And here result for those who are in a hurry.
We are going to rent a spot instance C3.4xlarge, 16 cores and 30 GB RAM.
"Spot" means that in fact we will participate in the auction and set a price per hour of use of the machine, to have access to it for as long as demand does not increase. If the demand will increase and market price will exceed the one we made, the car from us "run away", and suddenly. It is for this reason (instability), many people are afraid to use spot instances, though they can greatly save compared instances "on demand". Same car, but in a more "stable" mode, cost about $0.85/hour, we spend four times less.
Now, about the types of machines. They are well described the AWS documentation, so choose the type With a machine that is optimized for calculations.
the
rent a car
For a start, register on the website Amazon Web Services. Here instruction will not write — as usual, it will be necessary only to confirm by telephone, and via e-mail. The account will have a credit card bind, but if you are afraid of the expenses, you can instance m4large (2 CPU, 8 Gb RAM) to take over the $0.05/hour.
Go to your AWS console and find the service in Services EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)

The Spot Requests tab click on "Request Spot Instance".

Select the OS type, which will stand on a virtual machine. In General terms: Windows more among *Nix is not so important what to choose, let it be Ubuntu.

On the next tab, we are asked to choose the actual instance. Here pozalipaesh, posravnivaem (here all explained in detail) and scroll down to C3.4xlarge.

Then the most important thing is to set a price per hour of use dev. We see the current price in the selected regions.

If you see that You have prices much higher than in the screenshot, so now in the current surge region — change the region (in the upper right corner next to Your name). I have yet to successfully use the Frankfurt region, but it is possible to study the statistics to see which regions cheaper and stable prices.
The price is better to assign 1.5 times higher than the current market value of the instance in the region. In this scenario, the price will vary, but rarely exceed stated by You. Accordingly, so the machine is not often will "fall off."
Now connect the storage. Amazon treats thirty GB, so why not take all 30...

Tagging instance can be skipped. And then configure the ports. The main thing — to open the port that we will use under Jupyter server. Let traditionally, it will be 8888. Click "Add rule", leave the option "Custom TCP rule" and specify port 8888. Also added the HTTP and HTTPS protocols and speak, who can listen to ports. It is enough to choose the right Daw My IP.

In the next step generate the key (. pem file) that will us to identify when connecting remotely to the machine through SSH Protocol. It can be called whatever you like — the main thing after downloading to know where he lies in no case (!!!) don't put on GitHub or somewhere else online. Treat it almost like a file to the password of the credit card. Amazon recommends that you periodically update the. pem file (they can have 2 in each region, the second time you download the same key).

Finally, all confirm, wait a few minutes until the instance starts, and the EC2 on the tab "Instances" notice that something has appeared.

Select the displayed instance and click Connect. Amazon gives instructions on what to do next.
If You're under Windows, then You are reading the article does not end (usually, this is where the tutorials can be read "on Windows? Good luck!"). It is only necessary to read the instructions Amazon how to connect using Putty.
If You are under *NIX, then execute these 2 commands:
the
chmod 400 < PEM file name>.pem
ssh-i < PEM-file name>.pem ubuntu@<HOST>
First taking care that not every one who can access Your. pem file. The second is the actual connection to the virtual reality with its own unique host .
the
setting machines
If everything went smoothly, you as the user ubuntu will get to the terminal on the remote machine.
You can do anything, run any scripts, but we will focus on the instance setup for machine learning tasks with Jupyter. All commands described below, so that they were easier to understand (and to make sure there were no jokes in the style of rm-rf /) but the second time, and then we will start the bash script.
Download and install Miniconda. It is still much easier to Anaconda, and the necessary libraries we doustanovit (however, seaborn I have not flooded with Anaconda and everything is fine). We machine for a while, hardly more than a few hours, so no perfectionism — install everything into your home directory.
the
wget-c http://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
bash Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -b-p ~/miniconda
export PATH=~/miniconda/bin:$PATH
Now install all the libraries we want.
the
conda install-y pandas numpy scipy scikit-learn jupyter
You can, for example, and Vowpal Wabbit supply (smart linear model, which for large samples is sometimes considered a fast MapReduce implementations).
the
sudo apt-get -qq install vowpal-wabbit
It will not hurt and Git — the repository to download (I use Amazon S3 in this tutorial not considered).
the
sudo apt-get -qq install git
Create a certificate to log on Jupyter password — so much safer. Now do it with your hands, the second time this generated certificate will be used by the script.
the
openssl req-x509 -nodes -days 365 rsa:2048 -keyout jupyter.pem-out jupyter.pem
You will be prompted about the user information. In principle it is not necessary to fill in.
Now create the password for Jupyter server.
the
python
>>> from IPython.lib import passwd
>>> passwd('Sample password')
Appears the hash of Your password. Copy it.
the
'sha1:d0c0b7eb515e:f0e59fcd04aec7bb50886084ae8e1fa9a273f88e'
Finally, create a profile and start the IPython server, pre-specifying in the configuration file, what port we want to use and what addresses are allowed access. Specify the hashed password. You password will be different — need to insert your.
the
ipython profile create nbserver
printf "\n# Configuration file for ipython-notebook.\n
c = get_config()\n
# Notebook config\n
c.NotebookApp.ip = '*'\n
c.NotebookApp.password = u"sha1:d0c0b7eb515e:f0e59fcd04aec7bb50886084ae8e1fa9a273f88e"\n
c.NotebookApp.open_browser = False\n
c.NotebookApp.port = 8888\n" >> ~/.ipython/profile_nbserver/ipython_notebook_config.py
The last thing we do only on the remote machine — run IPython server.
(Why IPython and Jupyter not?.. Why certfile explicitly specified? The answer is simple: the crutches. Jupyter didn't want to see the. config file, and then not wanted him to see the settings of the certificate file. See if You and jupyter team starts and without an explicit configuration file and certificate).
the
ipython notebook --config="~/.ipython/profile_nbserver/ipython_notebook_config.py" --certfile=jupyter.pem
If all goes well, You'll see at the end read something like this.
the
[I 10:09:08.774 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/ubuntu
[I 10:09:08.775 NotebookApp] 0 active kernels
[I 10:09:08.775 NotebookApp] The Jupyter Notebook is running at: https://[all ip addresses on your system]:8888/
[I 10:09:08.775 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
the
Profit
Now go to browser on HOST:8888, where HOST is still the address of your instance. Attention! Protocol needs to be HTTPS, you may also need a confirmation certificate. (For example, in Chrome it is necessary to poke the "more" and confirm on the website).
Enter your password (there is, of course, not hashed, and "normal") and we see a pleasant picture — the file system of Jupyter.

Create a new Notepad and rejoice in the abundance of cores under the hood.

Now back to the terminal (our computer and not the remote machine) and let down on our instance of some dataset. For example, from the Kaggle competition "Forest Cover Type Prediction".
the
scp -i < PEM-file name>.pem <LOCAL_PATH_TO_DATA> ubuntu@<HOST>:/~
About machine learning, of course, interesting to talk to, but then we just run the Sklearn random forest on the raw data.

Note the parameter n_jobs — here we will use all 16 cores.
1,000 trees of maximum depth 15 learned ~ 5 seconds — 3 times faster than on my MacBook Air with 4 cores and 4 GB of memory. In large samples the difference, of course, will be significant.

the
same script
The process can be automated. Using the Amazon SDK for Python name boto can the backup spot instance runs a script to do that. But until we look at the scripts, which prepare the machine to work with Jupyter after it started.
All this in repository Github.
Just need 3 files:
the
-
the
- In config.txt write the path to your pem file, the host issued a fresh instance as well as the hashed password Jupyter server, which we created earlier.
thepemfile='<PEM-file>.pem' host='<HOST>' jupyter_password='<JUPYTER_PASSWORD>'
the - In remote_setup.sh add all that want to run on the remote machine.
the# Installing Miniconda wget-c http://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh bash Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -b-p /home/ubuntu/miniconda export PATH=/home/ubuntu/miniconda/bin:$PATH #Installing neccesary libraries conda install-y pandas numpy scipy scikit-learn jupyter #Can add whatever you want to install #sudo apt-get-qq install vowpal-wabbit #sudo apt-get-qq install git ipython profile create nbserver printf "\n# Configuration file for ipython-notebook.\n c = get_config()\n # Notebook config\n c.NotebookApp.password = u'"$1"'\n c.NotebookApp.ip = '*'\n c.NotebookApp.open_browser = False\n c.NotebookApp.port = 8888\n" > ~/.ipython/profile_nbserver/ipython_notebook_config.py ipython notebook --config="~/.ipython/profile_nbserver/ipython_notebook_config.py" --certfile=jupyter.pem
the - Script launch_remote_setup.sh just doing remote_setup.sh with the right settings on the remote machine.
thesource 'config.txt' scp-i $pemfile ./ipython.pem ubuntu@$remote_host:~ ssh-i $pemfile ubuntu@$remote_host 'bash -s' < remote_setup.sh $jupyter_password
In the correct directory, run:
the
sh launch_remote_setup.sh
5-7 minutes, that's all! You can work with Jupyter server.
Was about to pour some tea. But! A very important moment!
At the end of work stop your instance.
EC2 - > Instances - > Actions -> Instance State -> Terminate.
Terminate it and not stop (although the spot is only available). But if you run instances on demand stop is not completely off the car, can charge money for the data exchange.

Finally it is possible a little to discuss finances. A current account is checked at Amazon by clicking on their name and then on "Billing &Cost Management".
$0.25 / hour is about $25 per month if used 4 hours each weekday. Then everyone decides whether such spending.
Here to advertise and GitHub Student Developer's Pack — I personally, with their help received a certificate to Amazon for $110, still use it. In addition, for serious scientific projects is possible to obtain a grant from Amazon.
the
Conclusion
That's all for now. I think for some it was a jump-start to Amazon Web Services EC2. Let his servos to rest at night!
PS. Comments / advice / sharing of experience / s pull request are welcome.
Comments
Post a Comment