Jump Start to PowerShell (part I)
automation. Only PowerShell.

As a hobby, and if time permits, teach students in UKIT (former Moscow state College of information technology). At the moment I have little time to devote to his group of students, but it is enough to prepare a post here, on habré.
I am a system administrator in a large it company with a large dependency on it resources. Sort of activity seems to solve a large number of similar tasks to service users.
With the PowerShell language met about two years ago, but came to grips with them only a year later, not realizing at first its huge possibilities. In the article, first of all, I will focus on those who want to begin working with PowerShell, but don't trust him or doesn't know which side to approach this miracle.
Note: PowerShell is addictive.
Wikipedia tells us:
Look PowerShell cannot, like the command line:
powershell.exe
Or in the form application:
powershell_ise.exe
Powershell_ise.exe called the integrated scripting environment Windows PowerShell ISE. Allows you to work with language in a friendly environment with syntax highlighting, constructor teams, autocomplete commands by pressing TAB and other delights. Ideal for creating and testing scenarios.
To run powershell.exe or powershell_ise.exe enough to type the same name in the run line.
A PowerShell script file has the extension .ps1.

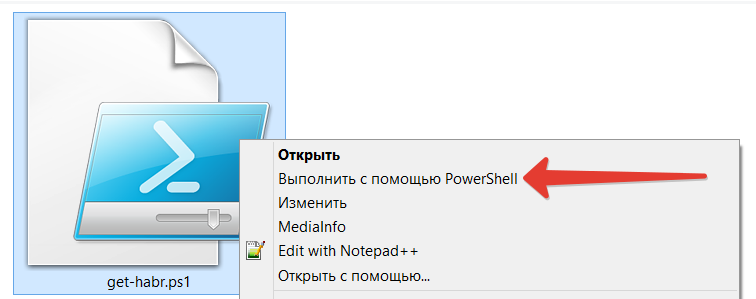
The script will not able to run in dual LMB. This was done deliberately in order not to harm the system by chance running the script.
To start, click RMB, select "Run with PowerShell":
Besides the fact that there is a limit of scripting LMB by default, the script execution in the system is prohibited, again, for the reasons described above — not to cause harm to the system. To check the current execution policy run the command:
the
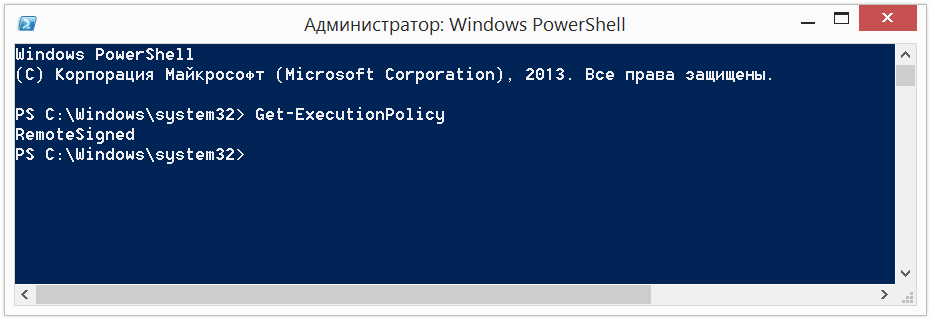
We will receive one of the following values. With high probability, if it were the first time, we get a Restricted.
the
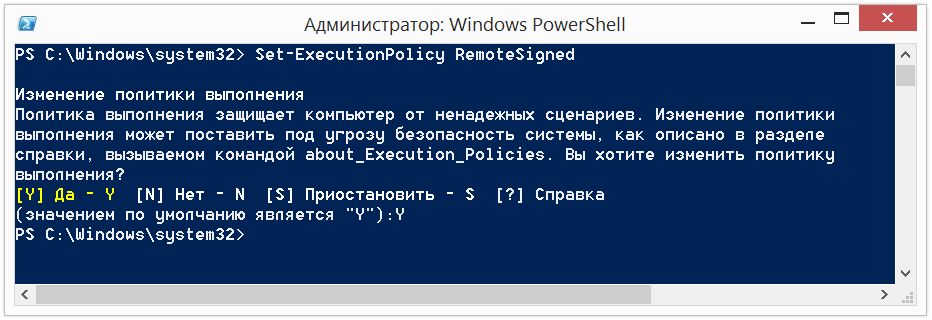
To execute and test lower policy RemoteSigned command:
the
the
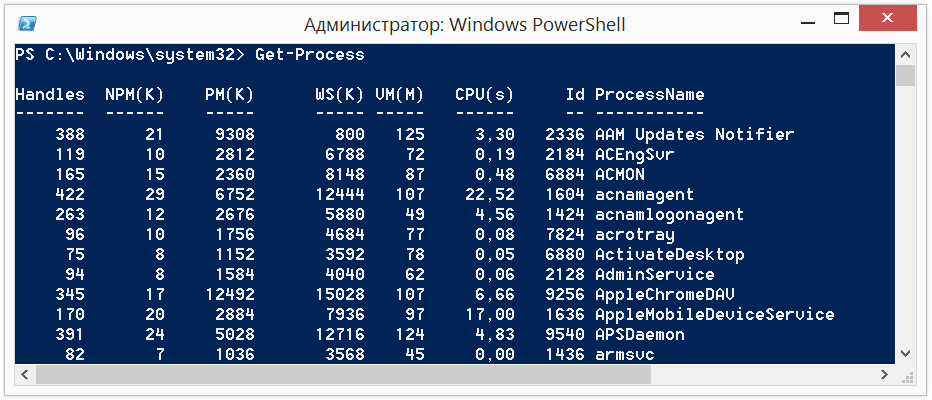
For example, to retrieve the current processes, we then use the command:
the
And get the result:
Try to execute:
the
the
Do not have to know by heart all the cmdlets. Get-Help will save the situation.
Information about all the available cmdlets can be obtained by entering the following command:
the
If we use the PowerShell ISE, we facilitate the development process.
Simply enter a dash "-" after introduced the cmdlet, and we get all the possible parameters and their types:

Try to run:
the
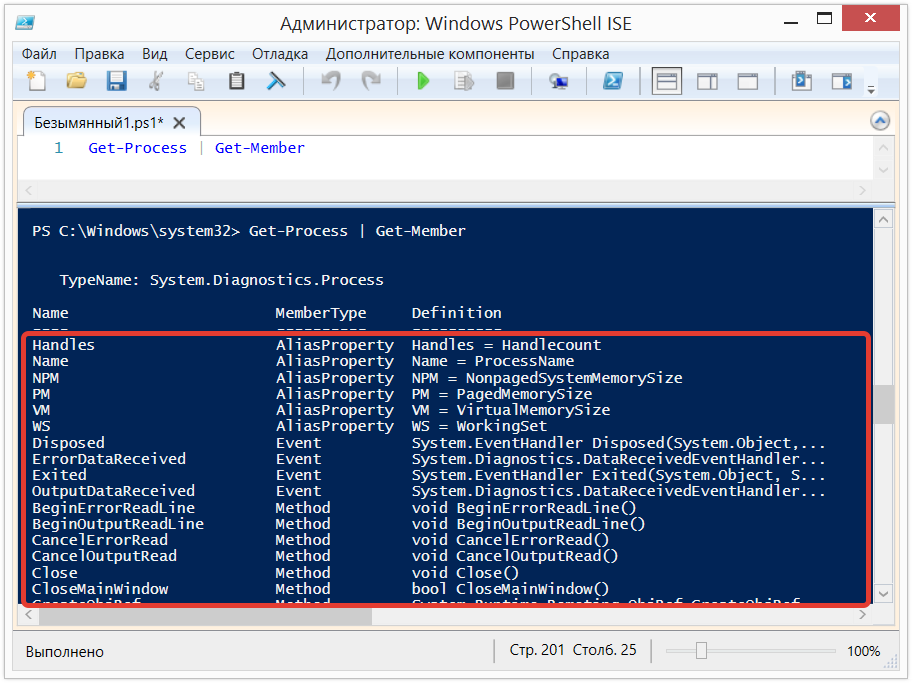
If, however, we will forget what the properties are for a cmdlet, run it through Get-Member:
the
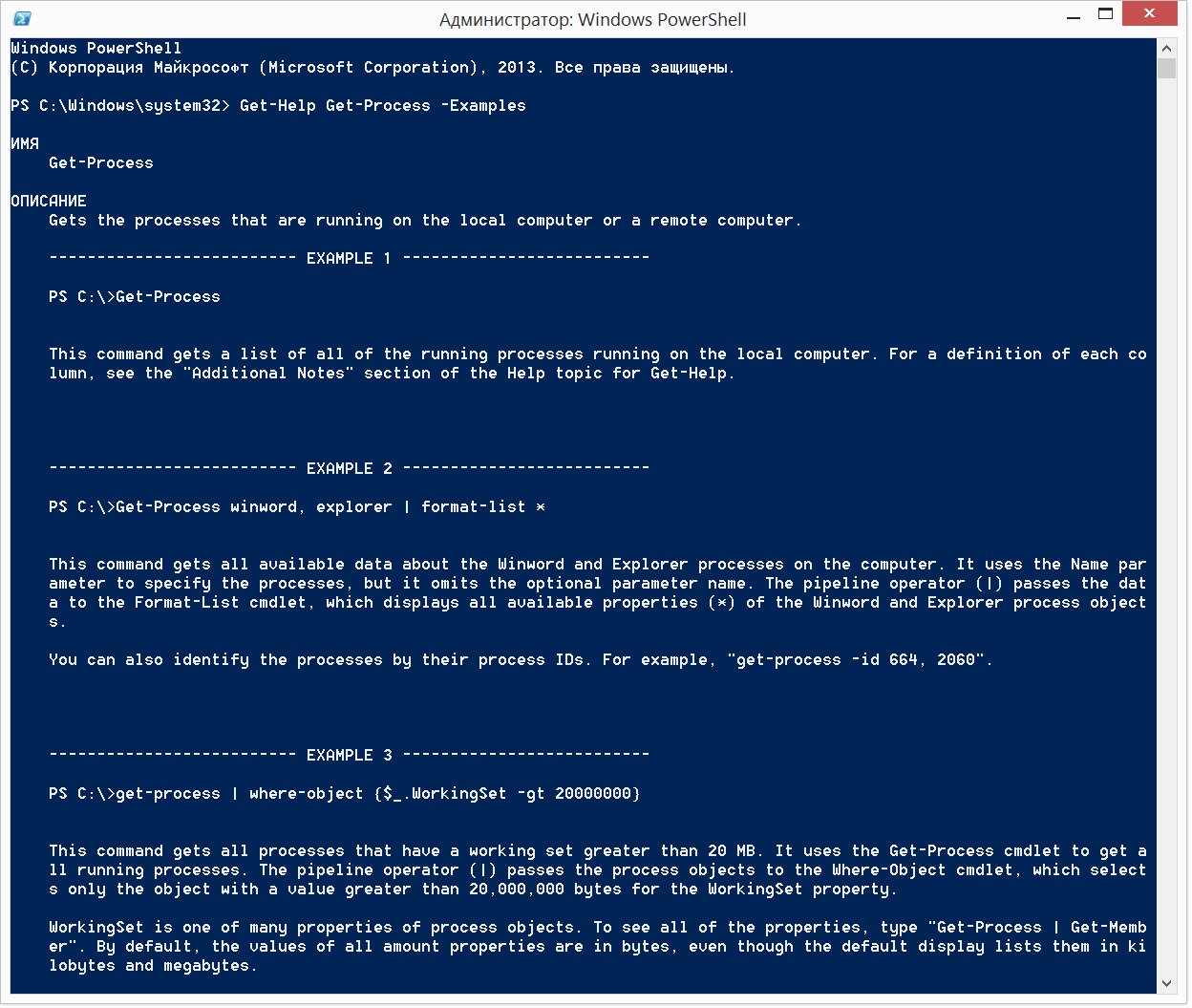
Not enough information? Refer to the help option -Examples:
the
Receive the description Get-Process, and even examples of usage:
the
Try to run:
the
Similar records:
the
Now stop the process:
the
Or this:
the
Earlier we said that the cmdlets are named according to the rule of Verb-Noun. Specify that the verb does not have to be Get. Besides the fact that we can obtain, we can set Set (remember, Set-ExecutionPolicy), run Start, to stop Stop, display, Out, create New and many others. The name of the cmdlet is not how it is limited and when we will contact you to create your own, we can call it as you want.
Try to run the output to a file:
the
By the way, can similarly be written as:
the
We all know the use of comments is good practice.
Comments in PowerShell are lower-case # and block <#... #>:

Notice on the code from the example:
the
For those familiar with WMI who does this on the good old VBScript, you remember how much code you have to write?
the
The pipeline (|) — sends output of one command as input to the processing of the other team. We used the pipeline earlier, getting all properties of an object or, in the previous example, selecting from the dataset only the field Caption.
To understand the principle of the conveyor belt, you can go through the code:
the
What will happen: get all service (Get-Service), to transfer all received the service to sort to the Sort-Object cmdlet and specify that you want to sort them by Status. On output, we first get all the service status Stop and then all services with the status Running.
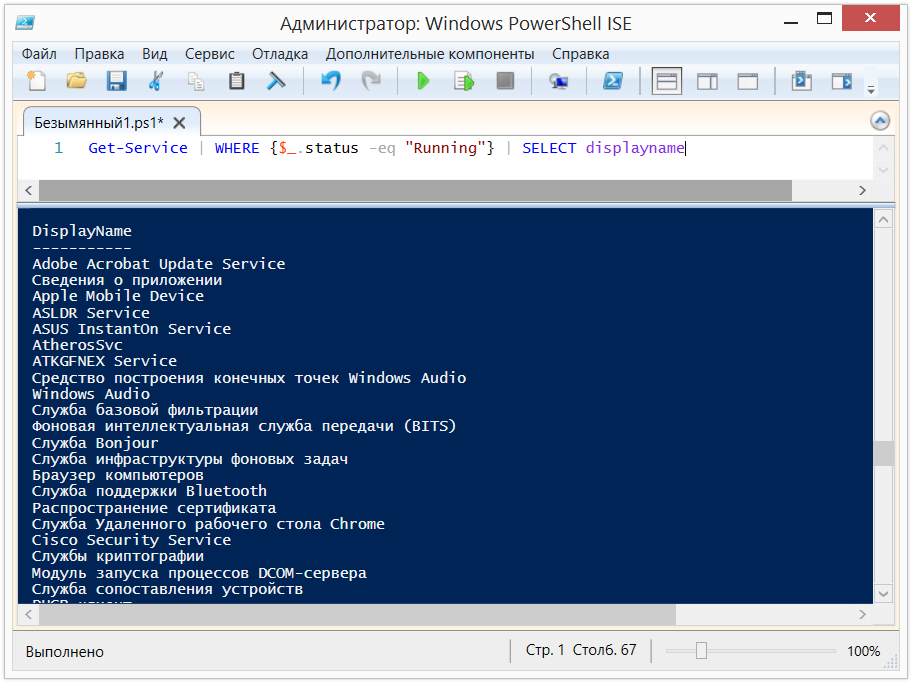
In the example below we first get all the running services. After the first conveyor, are passed for each item, select only those services that have the status Running and the second conveyor pick and choose what you want the output to see only the displayname of services:
the
In the example we use $_. This record means the current item in the pipeline.
In this part we learned how to start PowerShell, I understood the execution policy of scripts. Understand what the cmdlets that know how to pass them through the pipeline and how to get their properties. If we forget, be sure to Get-Help.
All this knowledge is needed in order to make the first leap into the language. Believe me, much more interesting!
the
Article based on information from habrahabr.ru

Preface
As a hobby, and if time permits, teach students in UKIT (former Moscow state College of information technology). At the moment I have little time to devote to his group of students, but it is enough to prepare a post here, on habré.
I am a system administrator in a large it company with a large dependency on it resources. Sort of activity seems to solve a large number of similar tasks to service users.
With the PowerShell language met about two years ago, but came to grips with them only a year later, not realizing at first its huge possibilities. In the article, first of all, I will focus on those who want to begin working with PowerShell, but don't trust him or doesn't know which side to approach this miracle.
Note: PowerShell is addictive.
Introduction
Wikipedia tells us:
Windows PowerShell is an extensible automation tool from Microsoft, consisting of a shell with command line interface and accompanying scripting language.
Look PowerShell cannot, like the command line:

powershell.exe
Or in the form application:

powershell_ise.exe
Powershell_ise.exe called the integrated scripting environment Windows PowerShell ISE. Allows you to work with language in a friendly environment with syntax highlighting, constructor teams, autocomplete commands by pressing TAB and other delights. Ideal for creating and testing scenarios.
To run powershell.exe or powershell_ise.exe enough to type the same name in the run line.

A PowerShell script file has the extension .ps1.

The script will not able to run in dual LMB. This was done deliberately in order not to harm the system by chance running the script.
To start, click RMB, select "Run with PowerShell":

Besides the fact that there is a limit of scripting LMB by default, the script execution in the system is prohibited, again, for the reasons described above — not to cause harm to the system. To check the current execution policy run the command:
the
Get-ExecutionPolicy

We will receive one of the following values. With high probability, if it were the first time, we get a Restricted.
the
Restricted — no Scripts can be run;
AllSigned — Can be run only scripts signed by a trusted publisher. Before you run the scenario by a trusted publisher you will be prompted for confirmation;
RemoteSigned is Allowed to perform we created scripts and downloaded scripts signed by a trusted publisher.
Unrestricted — No restrictions, all scripts can be launched.
To execute and test lower policy RemoteSigned command:
the
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned

Start work
Cmdlet
the
-
the
- Cmdlets are PowerShell commands which provide different functionality; the
- the Cmdlets can be both system and custom built by anyone; the
- Cmdlets are named by rule, Verb-Noun, which simplifies their learning; the
- Cmdlets output their results as objects, or collections; the
- the Cmdlets can both receive data for processing and to pass data through the pipeline (about pipelines later); the
- After the cmdlets do not have to put ";", except when we execute multiple cmdlets in one line (Get-Process; Get-Services).
For example, to retrieve the current processes, we then use the command:
the
Get-Process
And get the result:

Try to execute:
the
Get-Service #to get status of the services running on the computers
the
Get-Content C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts #to retrieve the contents of the file. In this case, the hosts file
Do not have to know by heart all the cmdlets. Get-Help will save the situation.
Information about all the available cmdlets can be obtained by entering the following command:
the
Get-Help -Category cmdlet
If we use the PowerShell ISE, we facilitate the development process.
Simply enter a dash "-" after introduced the cmdlet, and we get all the possible parameters and their types:

Try to run:
the
Get-Service-Name p*
If, however, we will forget what the properties are for a cmdlet, run it through Get-Member:
the
Get-Process | Get-Member
#The "|" character is called a pipeline. Read about it below.

Not enough information? Refer to the help option -Examples:
the
Get-Help Get-Process -Examples
Receive the description Get-Process, and even examples of usage:

the
-
the
- the Cmdlets can have abbreviated names — aliases. For example, instead of Get-Help you can use just Help. To get all of the cuts run Get-Alias.
Try to run:
the
Start-Process notepad
Similar records:
the
start notepad
Now stop the process:
the
Stop-Process -Name notepad
Or this:
the
spps -Name notepad
Earlier we said that the cmdlets are named according to the rule of Verb-Noun. Specify that the verb does not have to be Get. Besides the fact that we can obtain, we can set Set (remember, Set-ExecutionPolicy), run Start, to stop Stop, display, Out, create New and many others. The name of the cmdlet is not how it is limited and when we will contact you to create your own, we can call it as you want.
Try to run the output to a file:
the
"Hello, Habr!" | Out-File C:\test.txt
& C:\test.txt
By the way, can similarly be written as:
the
"Hello, Habr!" > C:\test.txt
& C:\test.txt
Comments
We all know the use of comments is good practice.
Comments in PowerShell are lower-case # and block <#... #>:

Notice on the code from the example:
the
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem | SELECT Caption
For those familiar with WMI who does this on the good old VBScript, you remember how much code you have to write?
the
On Error Resume Next
strComputer = "."
Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:\\" & strComputer & "\root\cimv2")
Set colItems = objWMIService.ExecQuery("Select * from Win32_OperatingSystem",,48)
For Each objItem in colItems
Wscript.Echo "Caption:" &objItem.Caption
Next
Conveyor
The pipeline (|) — sends output of one command as input to the processing of the other team. We used the pipeline earlier, getting all properties of an object or, in the previous example, selecting from the dataset only the field Caption.
To understand the principle of the conveyor belt, you can go through the code:
the
Get-Service | Sort-Object-property Status
What will happen: get all service (Get-Service), to transfer all received the service to sort to the Sort-Object cmdlet and specify that you want to sort them by Status. On output, we first get all the service status Stop and then all services with the status Running.
In the example below we first get all the running services. After the first conveyor, are passed for each item, select only those services that have the status Running and the second conveyor pick and choose what you want the output to see only the displayname of services:
the
Get-Service | WHERE {$_.status-eq "Running"} | SELECT displayname
In the example we use $_. This record means the current item in the pipeline.

PostScript
In this part we learned how to start PowerShell, I understood the execution policy of scripts. Understand what the cmdlets that know how to pass them through the pipeline and how to get their properties. If we forget, be sure to Get-Help.
All this knowledge is needed in order to make the first leap into the language. Believe me, much more interesting!
to be Continued...
Additional information
the
-
the
- Jump Start into PowerShell (part II); the
- Download PowerShell v.5 for free without registration; the
- Wonderful course on MVA: Advanced scripting in PowerShell 3.0 (Jump Start). My advice is to look at the first 3 blocks, immerse yourself in the language, try to do a little some tasks and after a week see the remaining blocks. Russian subtitles; the
- Video in topic at TechDays;
Gallery of PowerShell scripts on Technet;
developer Blog PowerShell.
Comments
Post a Comment