NASA has developed a navigation system for interstellar travel

About two hundred years (until the invention of radio) sailors measured the height of the Sun and moon using a sextant. Information from two objects, it is sufficient to calculate the exact coordinates in space. Now NASA has applied the same principle to develop global positioning system in space. Instead of the Sun and moon space module NICER/SEXTANT will determine the direction of the neutron star, the coordinates and trajectories of which are known fairly accurately. Each of the 2,000 well-known pulsars — specific frequency of rotation and the magnetic field strength that allows you to create a space analogue of the GPS system.

the Use of the sextant in practice, author: Joaquim Alves Gaspar
The ordinary sextant is induced in the Sun/the moon manually, and the elevation angle of the lights is displayed on a special scale. After this, the Navigator must manually find two suitable lines of position in the reference and the point of intersection.

Space module NICER/SEXTANT from NASA, of course, will work fully automatically.
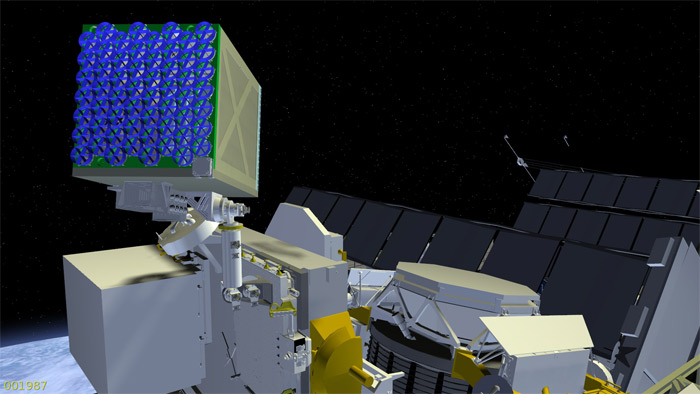
The system determines the x-ray sources (pulsars), and with the help of special reflectors determines the exact direction to them. NASA want to do on the module Autonomous integrated navigation system, which is able to operate without help from Earth.

Ear reflectors NICER/SEXTANT
Module NICER/SEXTANT holds 56 telescopes and detectors that are required to record radiation of pulsars with high precision. This unit is slightly bigger than a refrigerator, plan to launch to the International space station in 2017. The project cost is approximately $55 million.
Comments
Post a Comment